
What Is Tg Temperature. The glass-transition temperature refers to the temperature at which polymers will be converted from an elastic state to a glassy state expressed by Tg. Glass Transition Temperature Tg is the point at which a material alters state going from a glass-like rigid solid to a more flexible rubbery compound. Ordinary PCB materials at high temperatures not only will be soften deformation melting and other phenomena but also the mechanical and electrical. And the boards will be hard and crisp which will affect hole and the electrical properties.
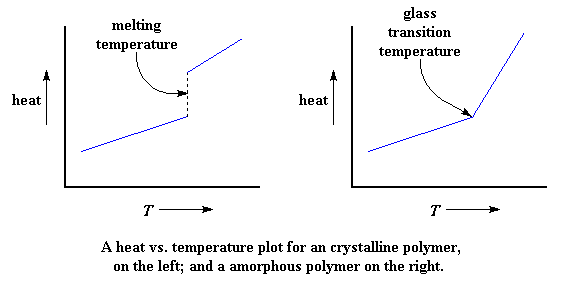
Tg is normally measured on a Differential Scanning Calorimeter DSC piece of whizzy equipment. The glass transition temperature T g of a polymer is the critical temperature at which the transition between glassy and rubbery state occurs 108. At this temperature the hard glassy state of an amorphous polymer converts into a rubbery state. Specifically the thermosetting polymers undergo this conversion while thermoplastic polymers undergo melting rather than converting into a rubbery state. Glass Transition Temperature Tg is the point at which a material alters state going from a glass-like rigid solid to a more flexible rubbery compound. In the hot state high Tg FR4 will have better mechanical and chemical resistance to heat and moisture than standard FR4.
The temperature point is called the glass transition temperature Tg.
The glass transition temperature T g of a polymer is the critical temperature at which the transition between glassy and rubbery state occurs 108. The standard FR4 Tg is between 130 140C the median Tg is 150 C and the high Tg is greater than 170C. Over the years we have all developed a set of assumptions about Tg that affect how we think about the design and manufacture of boards. TG of polymers or TG polymers is the glass transition temperature. It is also defined as a temperature at which amorphous polymer takes on characteristic glassy-state properties like brittleness stiffness and rigidity upon cooling. The use temperature T use for practical applications such as coatings and adhesives is generally required to be below the glass transition temperature so that the material at use is in rigid solid state.