What Is A Dilute Alkali. Dilute solutions of alkali metals in liq. Answer verified by Toppr Upvote 0. The salt of a carboxylic acid. Reaction of a metallic alkali base with a fat or.

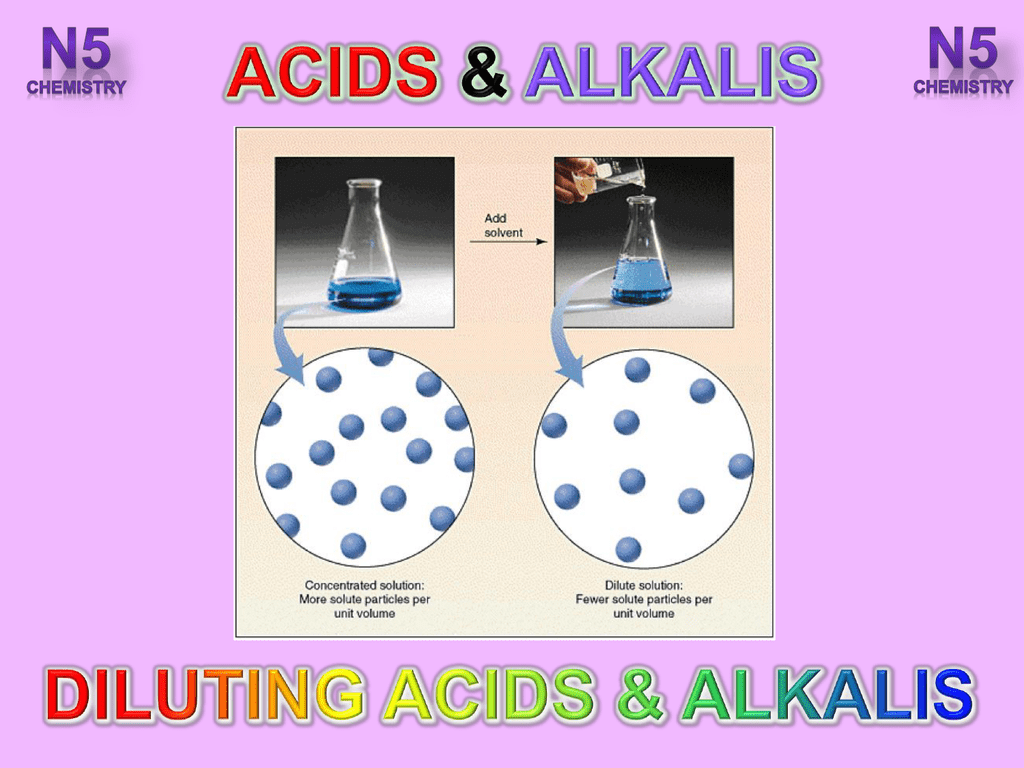
A tenfold dilution of hydrochloric acid will change its pH by 1 pH unit as will a tenfold dilution of sodium hydroxide. Biotransformation of lignin to lipids is challenging due to lignins recalcitrant nature as a phenolic heteropolymer with a nonuniform structure that imparts rigidity and recalcitrance of plant cell walls. A dilute alkali pretreatment NaOH was used to remove lignin and some hemicelluloses as well as to efficiently increase the accessibility of enzymes to the cellulose in Amur silvergrass. Oil to form soap. This does not mean the same as concentrated or dilute. The reactions are one-way rather than reversible and the products are easier to separate.
Dilute solutions of alkali metals in liq.
A dilute acid is that in which the concentration of the water mixed in the acid is higher than the concentration of the acid itself. This is the usual way of hydrolyzing esters. Oppositely treatment with dilute alkali has shown lower performances under the conditions explored most likely given the relatively significant lignin content suggesting that the use of stronger alkali regime with the associated drawbacks is unavoidable to improve the performance of this treatment. When alkalis are diluted the pH goes down toward 7. A dilute acid unlike a concentrated acid will ionize to a greater degree in their solution higher percent dissociation with decreasing concentration. A tenfold dilution of hydrochloric acid will change its pH by 1 pH unit as will a tenfold dilution of sodium hydroxide.