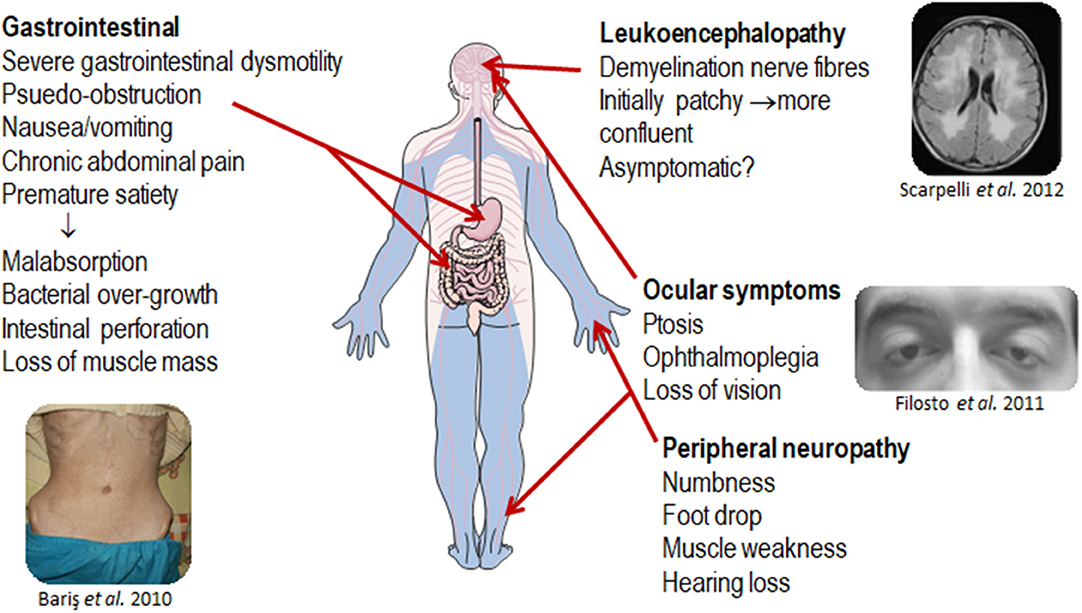
Mitochondrial Neurogastrointestinal Encephalopathy Treatment. Mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy MNGIE is a clinical syndrome that has been exclusively associated with autosomal recessive mutations in TYMP the gene encoding thymidine phosphorylase TPThe clinical hallmarks of MNGIE are ptosis ophthalmoparesis cachexia gastrointestinal dysmotility peripheral neuropathy and leukoencephalopathy evident on brain MRI. A case report and review of literature. 1 TYMP encodes for thymidine phosphorylase TP which catabolizes thymidine dThd and deoxyuridine dUrd into their respective bases. Hematopoietic stem cell transplant hSCT is the best studied treatment modality and has been shown to provide a durable decrease in circulating nucleosides and sustained clinical improvement.

11 Although formal guidelines for hSCT are in place for MNGIE 12 the decision to proceed with treatment is complex because of the high-risk nature of the treatment and the debilitated state most patients are in by the. MNGIE is clinically diagnosable because of a distinctive tetrad of gastrointestinal dysmotility progressive external ophthalmoplegia demyelinating neuropathy and. Mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy. Mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalopathy MNGIE is a rare autosomal recessive condition. Objective To study the effect of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis on nucleoside levels and clinical course in a patient with mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy MNGIE. Mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy MNGIE is a clinical syndrome that has been exclusively associated with autosomal recessive mutations in TYMP the gene encoding thymidine phosphorylase TPThe clinical hallmarks of MNGIE are ptosis ophthalmoparesis cachexia gastrointestinal dysmotility peripheral neuropathy and leukoencephalopathy evident on brain MRI.
Platelet transfusion hemodialysis peritoneal dialysis or allogeneic hematopoietic stem.
The major features of MNGIE disease can appear anytime from infancy to adulthood but signs and symptoms most often begin by age 20. Objective To study the effect of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis on nucleoside levels and clinical course in a patient with mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy MNGIE. Hirano M Nishigaki Y Martí R. 1 TYMP encodes for thymidine phosphorylase TP which catabolizes thymidine dThd and deoxyuridine dUrd into their respective bases. Management is primarily supportive and includes attention to swallowing difficulties and airway protection. Mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy MNGIE is a clinical syndrome that has been exclusively associated with autosomal recessive mutations in TYMP the gene encoding thymidine phosphorylase TPThe clinical hallmarks of MNGIE are ptosis ophthalmoparesis cachexia gastrointestinal dysmotility peripheral neuropathy and leukoencephalopathy evident on brain MRI.