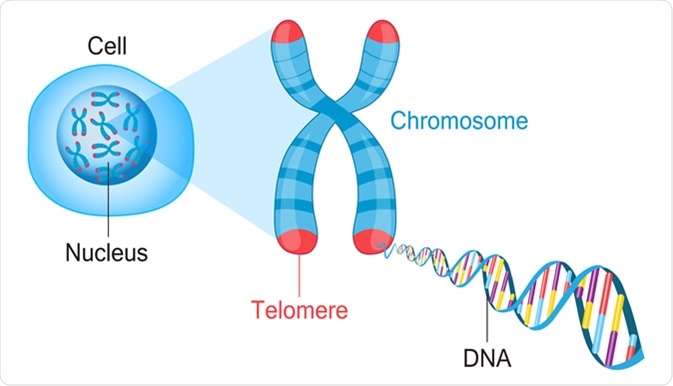
End Of Chromosomes Telomeres. Telomeres disguise the chromosome ends in eukaryotes The ends of linear eukaryotic chromosomes must not be perceived by the cell as broken DNA ends. Generally longer telomeres are associated with health and longevity. Telomeres are also thought to. They keep the ends of the various chromosomes in the cell from accidentally becoming attached to each other.

Telomeres are repetitive DNA sequences that protect the ends of each chromosome. However this important function for telomeres in chromosome end protection can be lost as telomeres shorten with cell division in culture or in self-renewing tissues with advancing age. At the ends of each of your chromosomes are stretches of DNA called telomeres. If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website. Chromosomes were unstable and prone to rearrangements and fusion whereas the chromosome ends were protected from such events12. Telomeres shorten with every cell division due to the end replication problem and with DNA damage.
They are made up of short tandem repeats rich in GC base pairs that may differ in sequences across different species.
Telomeres are the caps at the end of each chromosome that protect your DNA from unraveling or fraying. Generally longer telomeres are associated with health and longevity. Telomeres protect the end of the chromosome from DNA damage or from fusion with neighbouring chromosomes. Telomerase is a reverse transcriptase enzyme that carries its own RNA molecule eg with the sequence 3-CCCAAUCCC-5 in Trypanosoma brucei which is. They keep the ends of the various chromosomes in the cell from accidentally becoming attached to each other. The telomeres of humans consist of as many as 2000 repeats of the sequence 5 GGTTAG 3.